copy from http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=313915
Three types of authentication: User, App, Server-to-Server
User Authentication:
- Windows claims-based authentication ( NTLM, KerberosAD , basic)
- Forms-based authentication
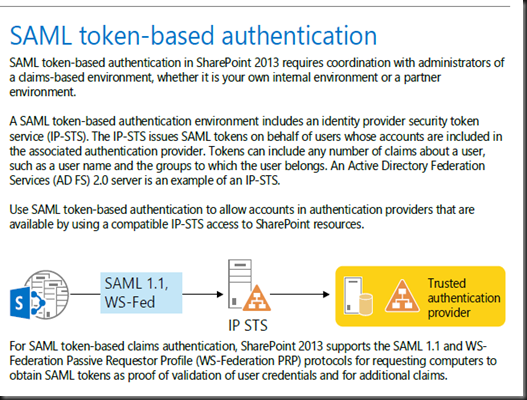
- SAML token-based authentication
The key elements of SAML token-based authentication are the following:
- Configure the IP-STS with the set of authentication providers (such as AD DS, databases, and others) corresponding to organization and partner accounts.
- Configure the IP-STS with the set of relying parties corresponding to the web applications that use SAML token-based authentication and claims mappings.
- Configure the SharePoint 2013 farm with the token signing certificate of the IP-STS, the corresponding claims mappings as done on the IP-STS, and the name of the IP-STS as a trusted security token issuer.
- Configure the web application with the name of the IP-STS as a SAML identity provider.
- *Identity Provider STS (IP-STS) sts=security token service
App Authentication:
- Low-trust Apps ( trust low-trust apps, you must have an Office 365 subscription > relies on the Windows Azure Access Control Service (ACS)
- High-trust Apps( for Internet hosts )
Server-to-Server Authentication
Server-to-server authentication enables a new set of functionality and scenarios that utilize cross-server resource sharing and access, including the following:
- eDiscovery Discover and place holds on content in the SharePoint farm, in Exchange Server 2013, on file shares, and in other SharePoint farms.
- Exchange task synchronization Allows users to synchronize SharePoint Server 2013 and Project Server tasks with Exchange Server 2013 and have them appear in Outlook 2013.
- Site mailboxes Provides SharePoint Server 2013 users with team email, hosted by Exchange Server 2013, on a SharePoint site.
- SharePoint 2013 Hybrid Federated search, Business Connectivity Services, and Duet Online between an on-premises SharePoint 2013 farm and SharePoint Online.